Orthopedic Surgery
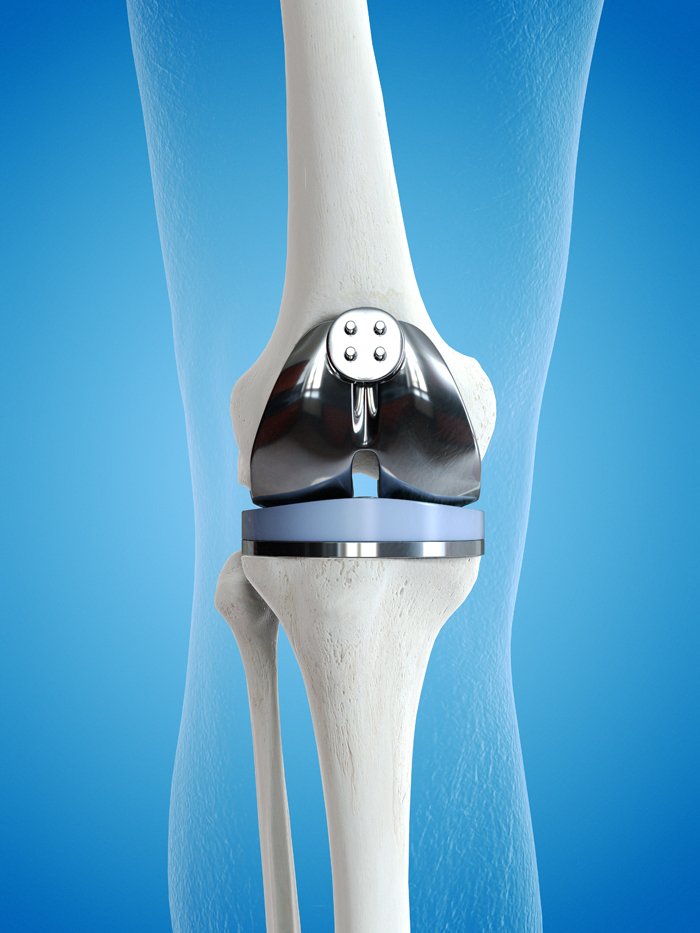
Knee Replacement
Knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a medical procedure performed to alleviate severe knee pain and disability caused by conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or traumatic injuries. During the surgery, the damaged or diseased parts of the knee joint are replaced with artificial implants made of metal, plastic, or a combination of both. The procedure aims to restore proper knee function, reduce pain, and improve the patient’s overall quality of life. Knee replacement surgery is typically considered when conservative treatments, such as medication and physical therapy, have proven ineffective in managing the debilitating symptoms. Advances in surgical techniques and implant technology have contributed to the success and durability of knee replacement procedures, making them a common and effective solution for individuals experiencing significant knee joint issues.
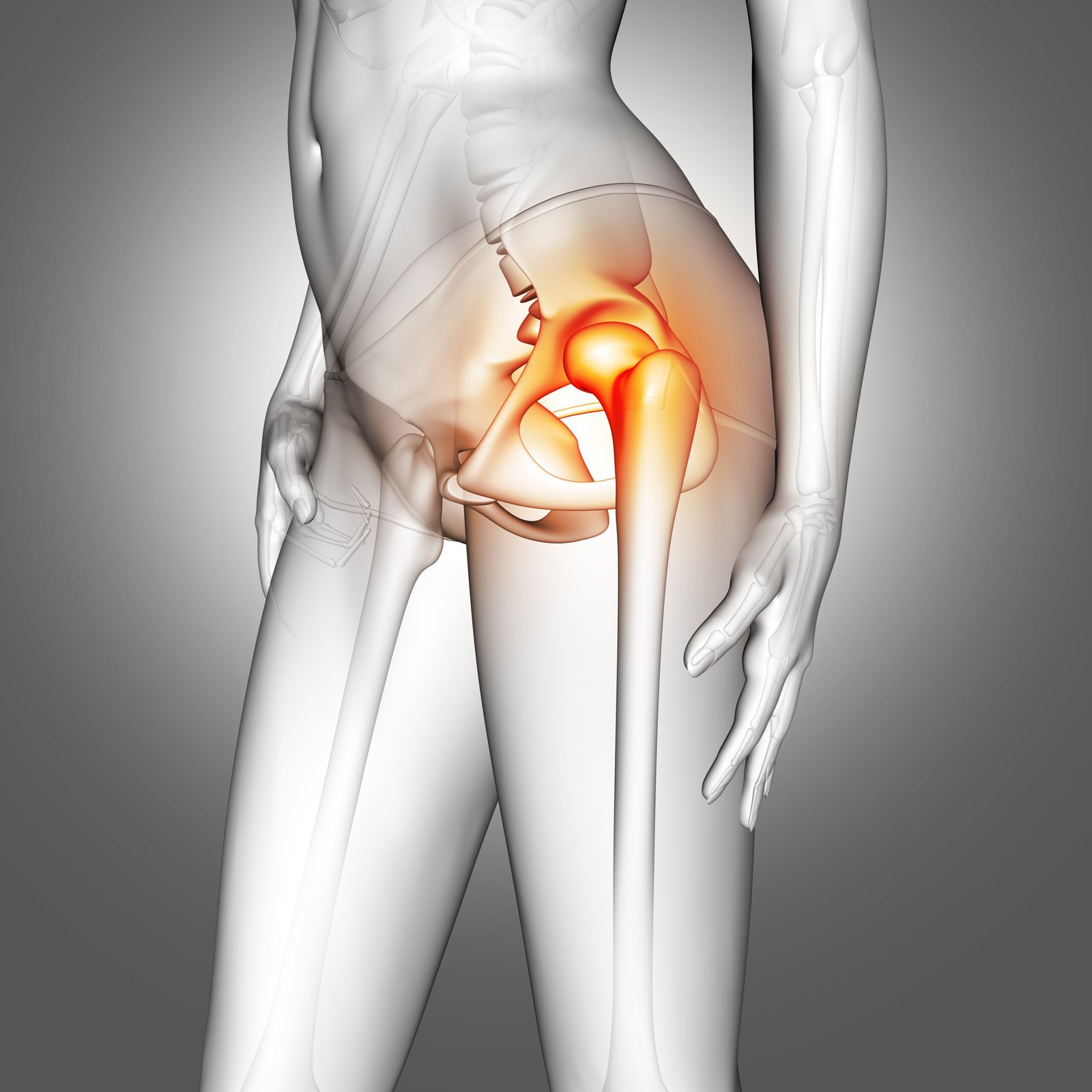
Hip Replacement
Hip replacement surgery, also known as hip arthroplasty, is a medical procedure designed to relieve pain and improve mobility in individuals with damaged or deteriorated hip joints. The surgery involves replacing the damaged parts of the hip joint with artificial implants made of metal, ceramic, or plastic components. This procedure is commonly recommended for patients suffering from conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or hip fractures. The surgery aims to restore the natural function of the hip, alleviate pain, and enhance overall quality of life. Recovery typically involves a period of rehabilitation and physical therapy to help patients regain strength and mobility in the hip joint, allowing them to return to a more active and pain-free lifestyle.
Joint Dislocation Treatment
Joint dislocation treatment often involves surgery to reposition the displaced joint and stabilize it for optimal healing. The primary goal of the surgical intervention is to restore the joint to its normal alignment, thereby allowing for proper function and preventing long-term complications such as chronic instability or arthritis. The procedure typically begins with the administration of anesthesia to ensure the patient’s comfort. The surgeon then carefully manipulates the dislocated joint back into its correct position, a process known as reduction. In some cases, additional measures, such as the use of screws, plates, or other fixation devices, may be employed to secure the joint and promote stability during the recovery period. Post-surgery, rehabilitation and physical therapy play a crucial role in restoring strength, flexibility, and functionality to the affected joint, facilitating a comprehensive recovery for the patient. The specific approach to joint dislocation treatment may vary depending on the type and severity of the dislocation, as well as individual patient factors.
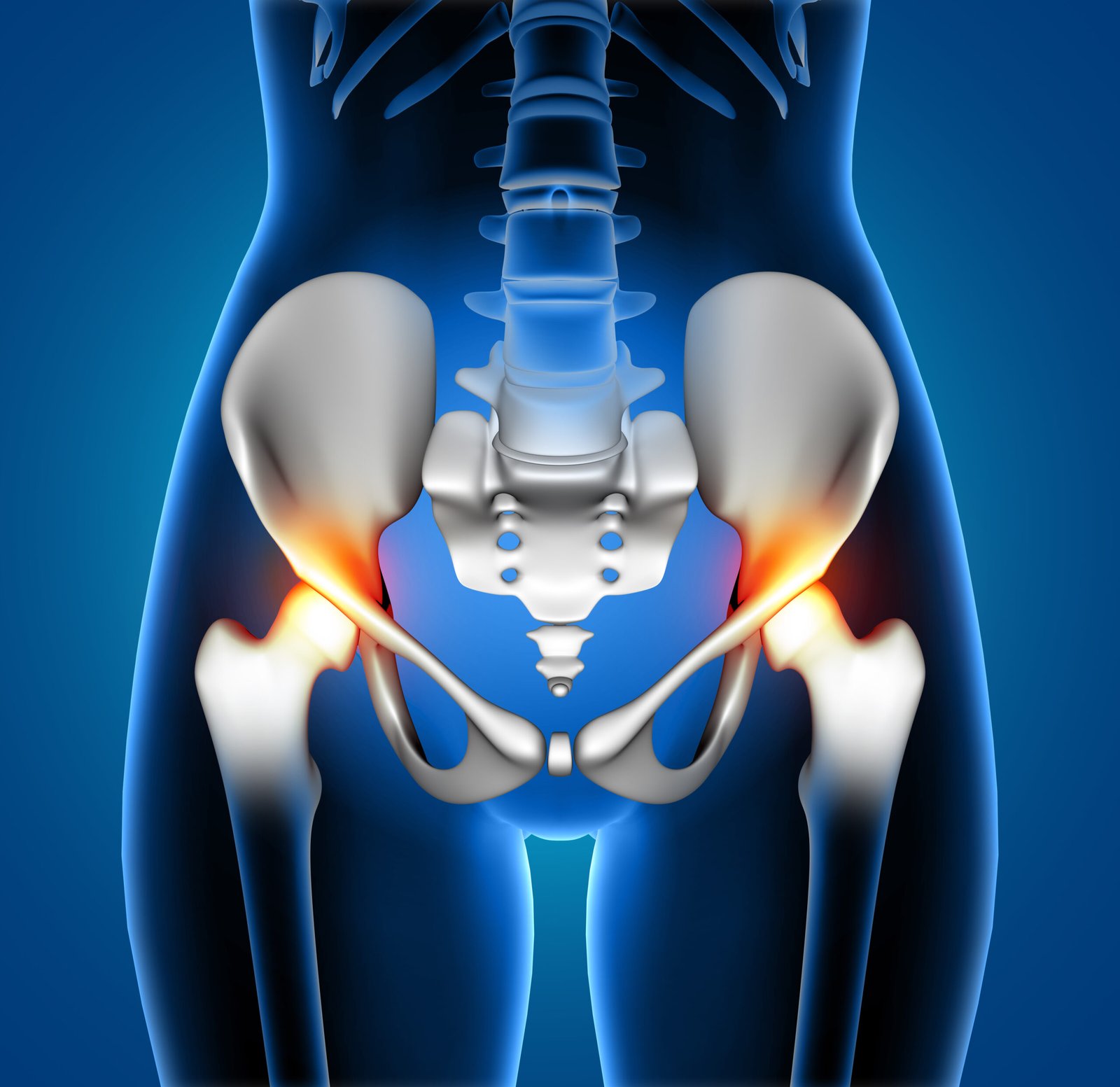
Hip Resurfacing
Hip resurfacing surgery is a medical procedure designed to address hip joint pain and dysfunction, particularly in patients with hip arthritis. Unlike traditional hip replacement, hip resurfacing preserves more of the patient’s natural bone by capping the femoral head with a metal prosthesis instead of removing and replacing it entirely. This technique is often considered for younger, more active individuals who may outlive a traditional hip replacement and require future revisions. The procedure involves reshaping the damaged bone and fitting it with a metal implant, creating a smoother joint surface. While hip resurfacing can offer increased stability and range of motion, it is not suitable for everyone, and the decision to undergo this surgery should be carefully evaluated based on the patient’s age, bone quality, and overall health. As with any surgical intervention, potential risks and benefits should be thoroughly discussed between the patient and their healthcare provider.
Knee Osteotomy
Knee osteotomy is a surgical procedure designed to treat specific knee conditions, often performed to address issues such as osteoarthritis or certain deformities. During the procedure, the orthopedic surgeon strategically cuts and repositions the bones around the knee joint to redistribute weight-bearing forces, alleviating pressure on damaged or worn-out areas. This realignment aims to reduce pain, improve function, and potentially delay the need for more extensive interventions like total knee replacement. Knee osteotomy is typically considered for patients who have isolated damage to one side of the knee joint, preserving the unaffected side. The procedure requires careful planning and personalized adjustments based on the individual’s anatomy and the specific nature of their knee condition. Post-surgery, patients undergo rehabilitation to regain strength and mobility, with the ultimate goal of achieving improved knee function and a better quality of life.
